Health
All Stories
Psychologists discover that the way the brain perceives beauty differs between art or faces.
The positive steps we are taking to prevent disease might have a negative side effect.
The researchers say their findings support the idea that low biodiversity in modern living environments could lead to “uneducated” immune systems.
Researchers design microdevices that can gradually deliver medicine by latching on to intestines.
A new study shows you should put down the toilet lid when flushing to avoid coronavirus and other illnesses.
What is more important, that a treatment helps keep people healthy or that it meshes with our morals?
It’s a precautionary measure stemming from fears that mutated coronavirus strains may reduce the efficacy of future vaccines.
The researchers trained the model on tens of thousands of samples of coughs, as well as spoken words.
Work that can break down the body can also break down the mind.
A new study seeks to understand why the average body temperature is no longer 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit.
A growing body of research suggests COVID-19 can cause neurological damage in some patients.
Researchers develop the first objective tool for assessing the onset of cognitive decline through the measurement of white spots in the brain.
Most people believe themselves to be less at risk from COVID-19 than others similar to them, according to a recent UCL survey conducted in the U.S.
Tea and coffee have known health benefits, but now we know they can work together.
Instead of looking forward, we should be consulting the past.
Medicago is growing a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidate in a relative of the tobacco plant right now.
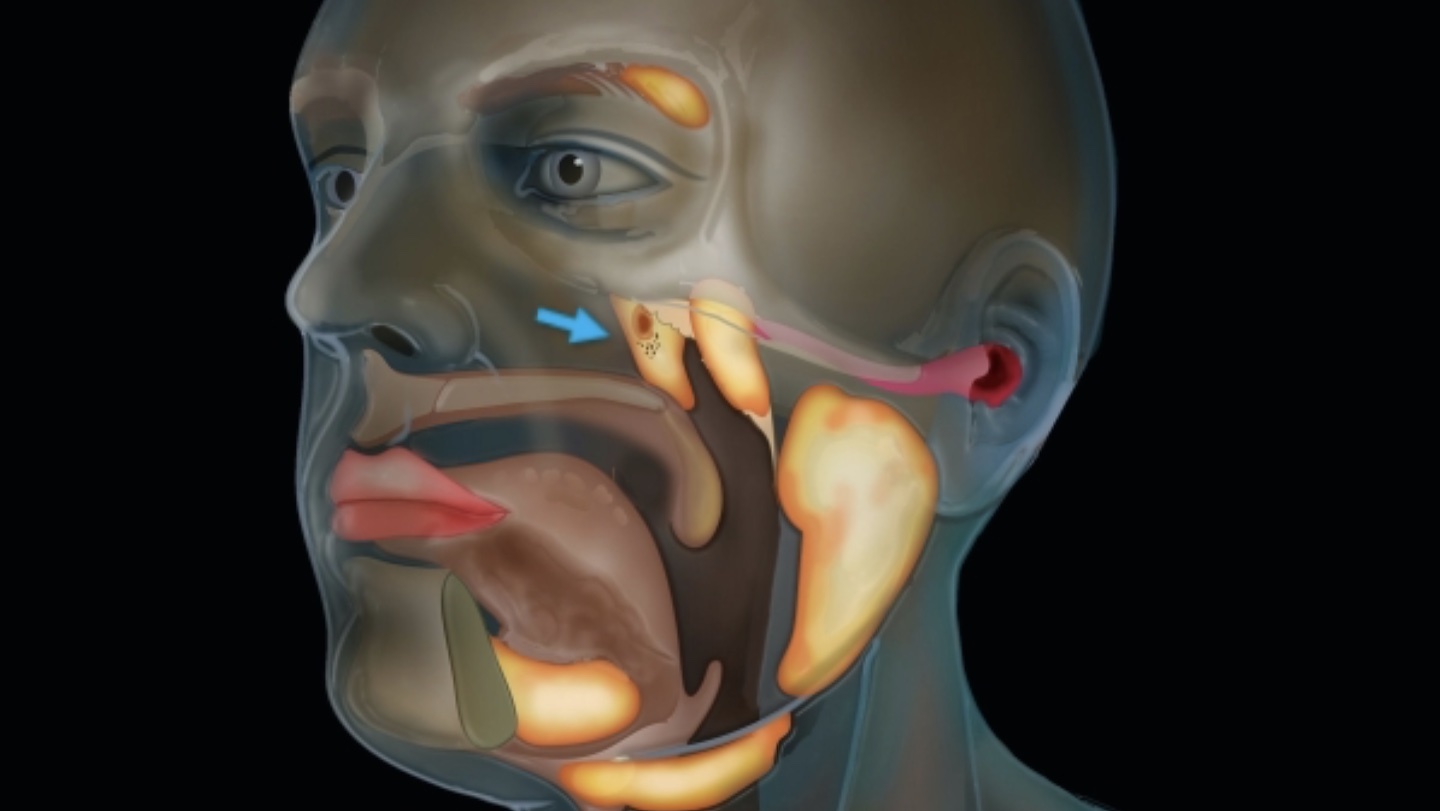
New cancer-scanning technology reveals a previously unknown detail of human anatomy.
Your health and the health of the planet are not indistinguishable.
A new study of nurses shows the importance of sleep—and staying aware on the job.
Northwell Health CEO Michael Dowling has an important favor to ask of the American people.
▸
1 min
—
with
Noise pollution is terrible for our health, yet we don’t discuss it often enough.
There has been a dramatic increase in abuse and misuse.
A series of recent studies found that people with healthy levels of vitamin D were less likely to contract COVID-19 and suffer severe complications from it.
94 percent of men in the study have this mutation, which explains why men are more likely to die.
Andrew Wakefield turned away from science and to the tabloids to spread his fabricated data.
We owe a lot to vaccines and the scientists that develop them. But we’ve only just touched the surface of what vaccines can do.
▸
17 min
—
with
In fact, the maximum human lifespan has barely changed since we arrived.
“Nothing but naked people: fat ones, thin ones, old, young…”
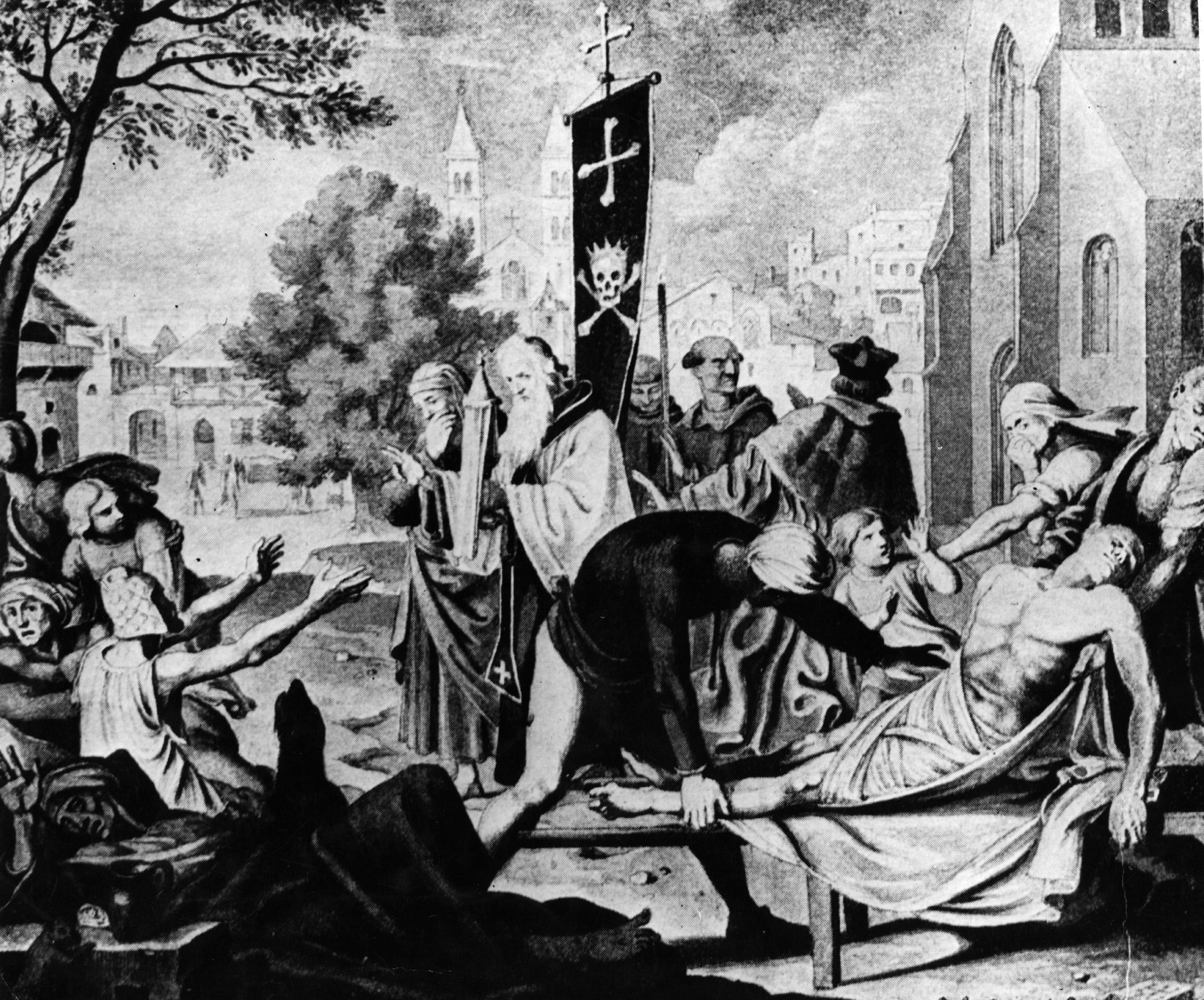
17th-century outbreaks of plague in Italy reveal both tensions between religious and public health authorities.