Neuropsych
All Stories
Parents will sometimes use children as weapons in their relationship battles — and the fallout can be devastating.
Ketamine’s remarkable effect bolsters a new theory of mental illness.
It could perform a speech recognition task with 78% accuracy.
The heart’s rhythms may play a larger role in shaping psychedelic experiences than previously thought.
Millions of people have had a near-death experience, and it often leads them to believe in an afterlife. Does this count as good proof?
Between the hedonic and eudaimonic life, there’s a happy medium to be found.
The aging brain is networked differently.
Even before birth, our brains are taking note of the languages we hear.
Your life’s memories could, in principle, be stored in the universe’s structure.
Some neuroscientists question whether the body can “keep score” of anything in a meaningful way.
Arieh Smith, a New York City-based polyglot who runs the YouTube channel Xiaomanyc, talks language-learning with Big Think.
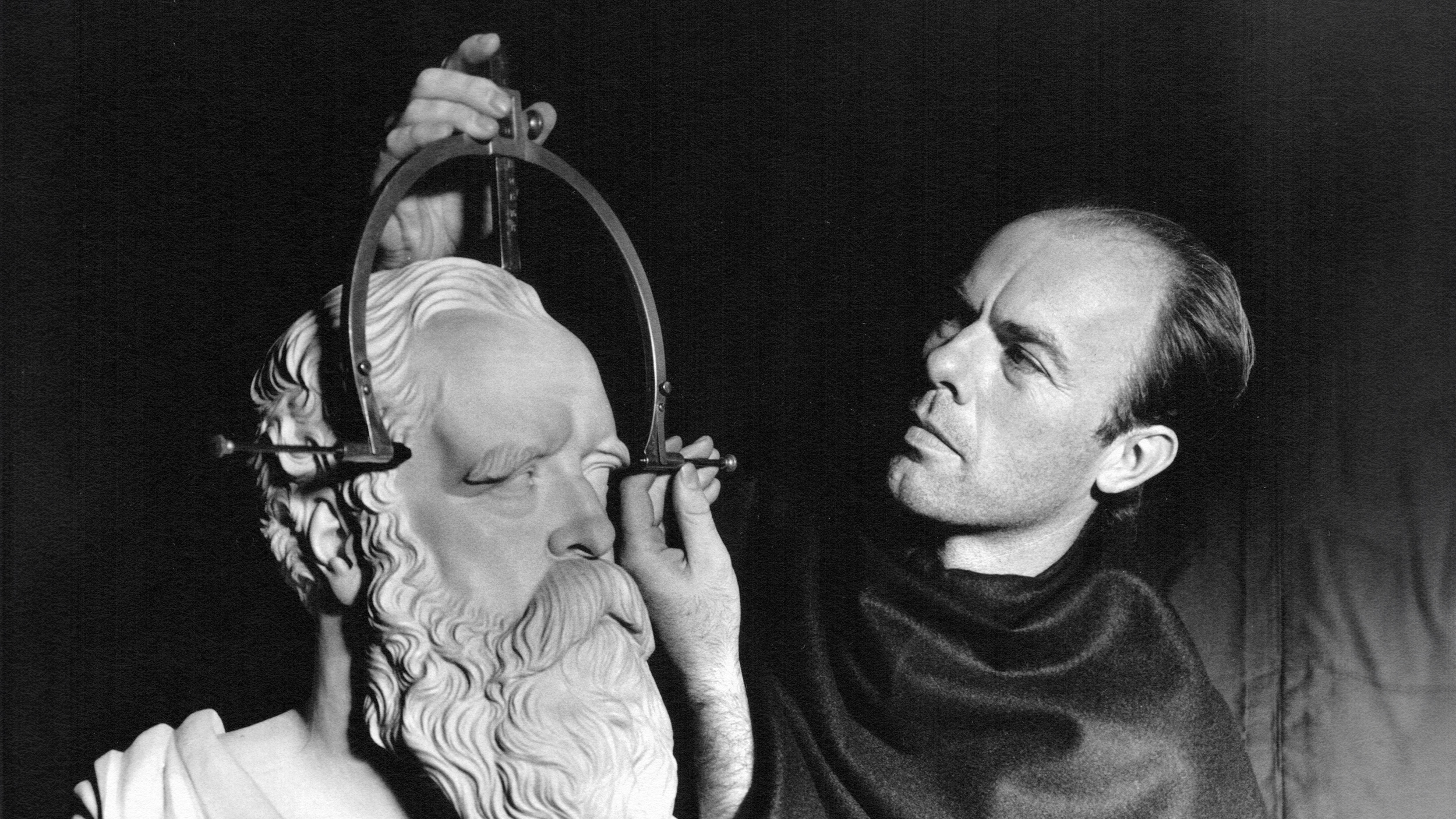
The pseudoscience phrenology swept the popular imagination, and its practitioners made a mint preying on prejudices, gullibility, and misinformation.
Instead of fear, his delusions bring him cheer. His psychiatrist embraces them.
After my father died, my journey of rediscovery began with the Czech language.
There are many things in life that cannot be improved with greater effort. Sometimes, life requires that you step back.
While executive function matures between 18 and 20 years of age, the brain keeps changing long afterward.
We are wired to value things more when we work hard at attaining them — even if, objectively, they aren’t worth that much.
We all have a place in our lives where we look the other way and pretend everything is fine. It’s a built-in excuse to act selfishly.
Lucid dreamers may have “privileged access to their inner world,” with “heightened awareness… to the outside world.”
Katie Kermode — a memory athlete with four world records — tells Big Think about her unique spin on an ancient technique to memorize unfathomably long lists of information.
What a long strange trip it’s been.
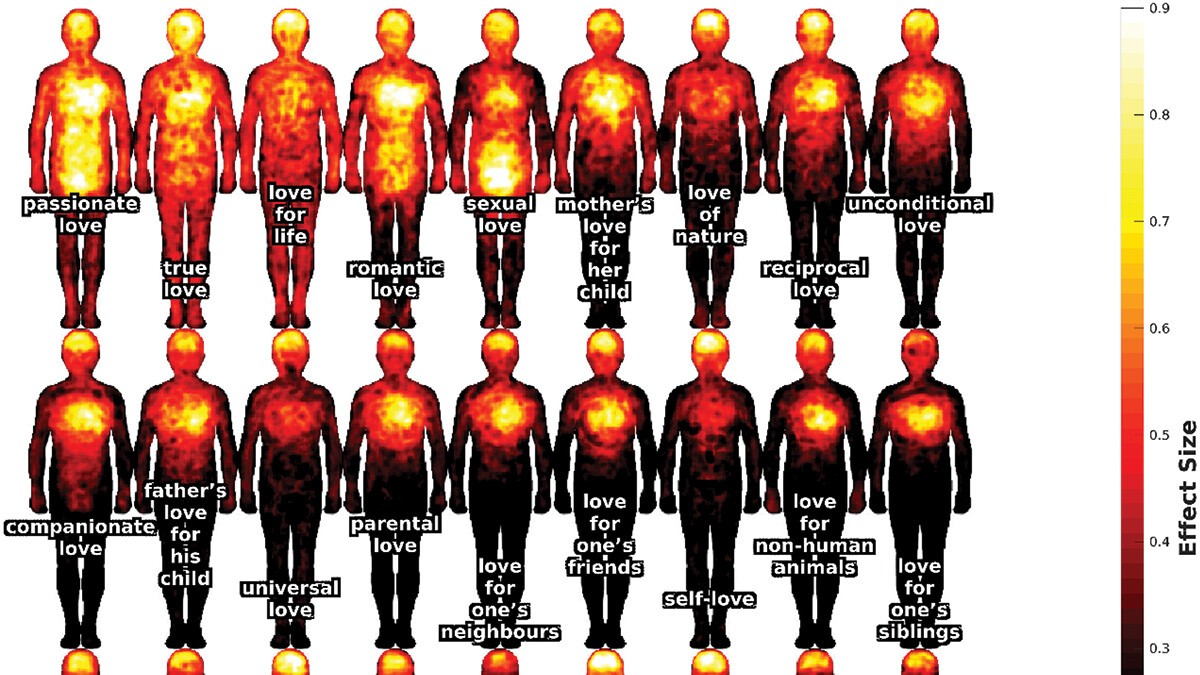
Survey data suggests that our bodily perceptions of love extend far beyond the heart.
If someone can make you feel insecure, incomplete, and inadequate, they then can present themselves as the solution you need.
A healthy lifestyle even protects those who are genetically predisposed to depression.
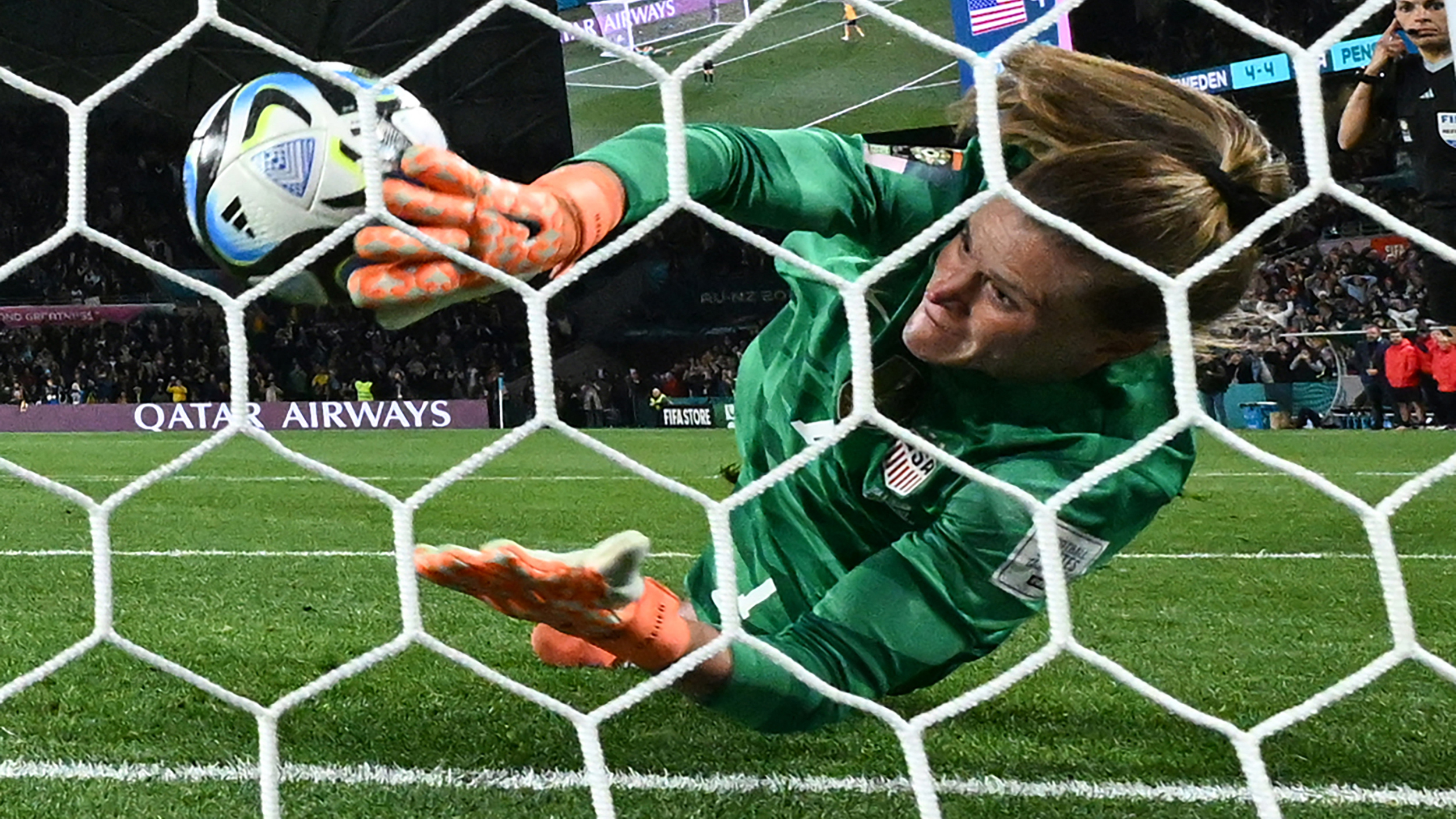
Goalkeepers have an enhanced ability to integrate auditory and visual information compared to other players.
Only about 10% of patients survive cardiac arrest. Of the ones who do, many have amazing stories to tell.
If you want to achieve new goals, harness your brain’s ability to change chemically, structurally, and functionally.
Chronic pain is often driven by brain processes that can be reprogrammed.